What is Botulinum Toxin?
Botulinum toxin is a purified protein derived from the bacterium Clostridium botulinum. Among the various types used in clinical settings, botulinum toxin type A is most commonly applied in cosmetic procedures due to its safety and effectiveness profile.
In aesthetic medicine, it is typically administered in small, controlled doses to temporarily relax targeted facial muscles. This helps reduce the appearance of dynamic wrinkles — lines that develop over time from repeated expressions such as smiling, frowning, or squinting.
Its mechanism of action involves temporarily blocking nerve signals that trigger muscle contractions. As a result, treated muscles stay at rest, reducing excessive movement and helping to soften the formation of deeper expression lines.
Beyond wrinkle reduction, botulinum toxin is also commonly applied to the masseter muscles (located near the jaw) to help manage jaw clenching, teeth grinding (bruxism), and the appearance of a broader or more prominent jawline.
Application and dosage may vary depending on factors such as individual facial anatomy, muscle activity, and treatment objectives, and should always be carried out in accordance with clinical protocols.
Common Aesthetic & Functional Applications
Upper Face Rejuvenation
Botulinum toxin is frequently used to reduce the appearance of facial wrinkles in areas such as:
Forehead
Frown lines between the eyebrows
Crow’s feet at the corners of the eyes
Lines around the lips or chin
By selectively relaxing specific muscle groups, botulinum toxin treatments may help soften wrinkles and can sometimes create a subtle lifting effect in the brow area, contributing to a more refreshed appearance.
Facial Contouring & Jaw Muscle Relaxation
Botulinum toxin is also commonly applied to the masseter muscles — the jaw muscles responsible for chewing and clenching. This may help individuals who experience:
Jaw clenching or teeth grinding (bruxism)
Tension-related discomfort in the jaw
A wider or more prominent jawline due to muscle bulk
Over time, decreased muscle activity may help relieve jaw tension while supporting a more balanced lower face appearance.
Medical Conditions
In some cases, botulinum toxin is also used in medical settings to help manage:
Chronic migraines
Excessive sweating (hyperhidrosis)
Certain muscle spasms (e.g., neck or eyelid)
Strabismus (eye muscle imbalance)
Use of botulinum toxin for medical indications is determined after clinical evaluation and should only be adminstered by licensed medical doctors.
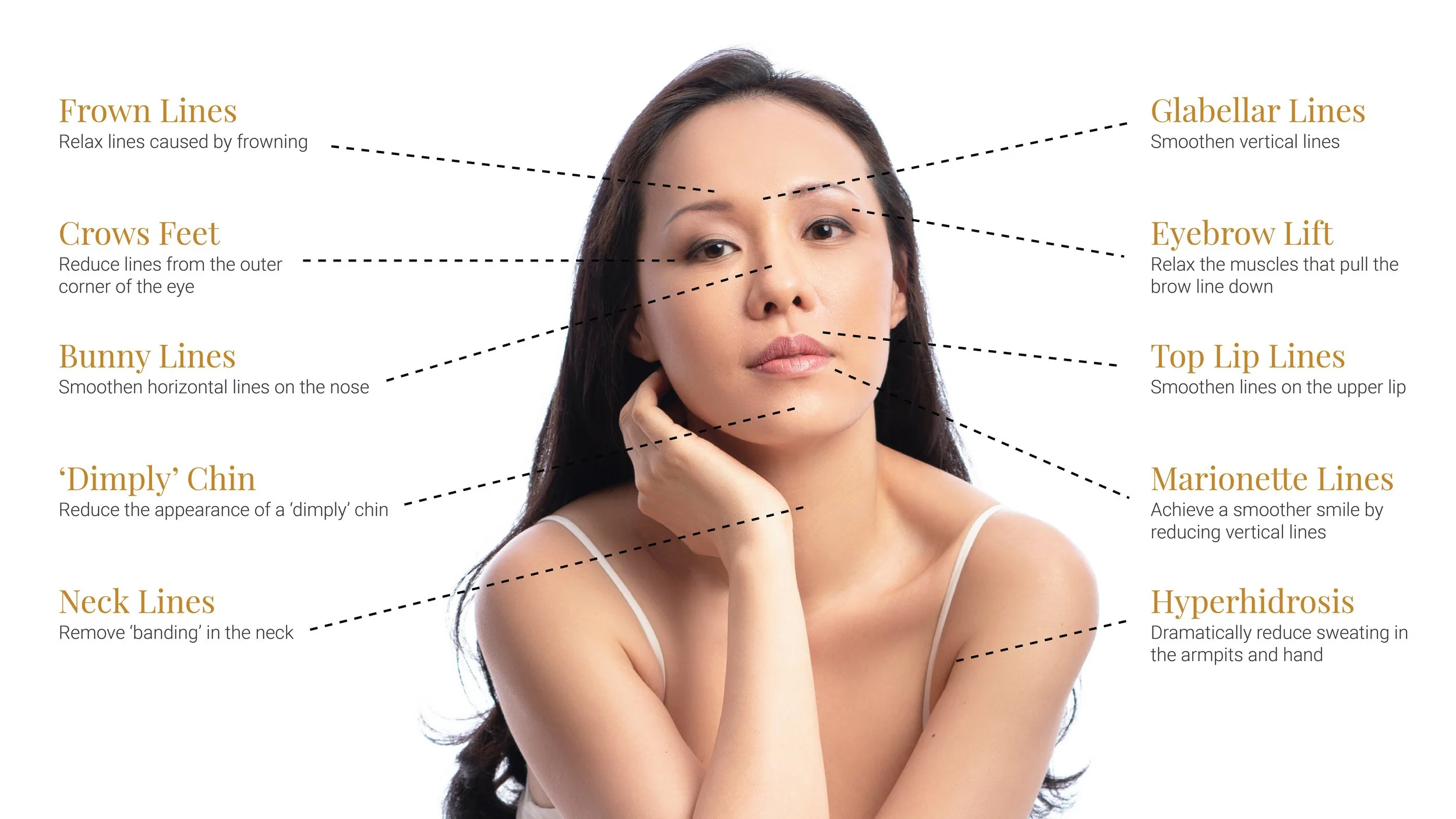
10 Areas Commonly Treated with Botulinum Toxin
Botulinum toxin is commonly administered in multiple facial and neck regions to address expression-related lines and muscle activity. These application zones represent commonly observed facial movement patterns and are selected based on individual muscle dynamics and aesthetic considerations.
Is Botulinum Toxin Right For You?
You may be a suitable candidate for botulinum toxin injections if you:
Notice visible facial lines caused by muscle movement
Experience brow heaviness or a tired appearance
Have a wide jawline or symptoms of jaw clenching
Show a gummy smile or high upper lip elevation
Struggle with persistent teeth grinding
Prefer a non-surgical approach to facial enhancement
Are exploring options for managing excessive sweating or certain neurological symptoms
A full assessment by a licensed medical doctor is required to determine suitability. Treatment plans and dosages are determined on an individual basis.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
When administered by licensed medical professionals, botulinum toxin injections have a well-documented safety profile. As with any medical procedure, there are potential risks, such as temporary discomfort, bruising, or unintended effects on surrounding muscles. These risks may vary depending on individual factors and practitioner expertise.
It is important that such procedures are conducted in licensed medical clinics by healthcare professionals trained in facial anatomy and injectable techniques. Treatment decisions should be based on clinical evaluation, not cost considerations.
-
Most individuals find botulinum toxin injections very tolerable. The procedure uses a fine needle, and the sensation is often described as a quick pinprick. While discomfort is generally minimal, topical numbing cream may be applied before treatment if preferred.
-
Some individuals may experience temporary side effects such as mild redness, tenderness, or bruising at the injection site, which typically resolves quickly.
Downtime is generally minimal, and many individuals resume normal activities shortly after, depending on personal response and treatment area.
-
Visible results typically begin to appear within 3 to 5 days after a botulinum toxin treatment.
The effects generally last around 4 to 6 months, depending on individual factors such as metabolism and muscle activity.
Overtime, our bodies naturally metabolizes the botox injection, leading to the slow return of muscle movement in the treatment area. Repeat treatments may be recommended to maintain desired effects, under medical supervision.
-
Botulinum toxin is generally not recommended during pregnancy or breastfeeding as a precautionary measure. This precaution is essential to safeguard the well-being of both the mother and the child, ensuring that potential risks or adverse effects are minimised during these critical stages of maternal and infant health.